Authentication
Apifon offers several ways to authenticate and authorize your application to connect with our REST API.
The supported options are either HMAC tokens or OAuth2 tokens.
Both of those options provide access to your account resources. For example you can have a component of your application using HMAC tokens for Authentication/Authorization purposes and another component using OAuth2 tokens, both of them accessing the same resources.
For configuring each of them please refer to the specific documentation.
HMAC Authentication
To make use of the REST API, you must supply with each request an authorization token in the HTTP header. The token (ApifonWS) at this point will be generated automatically through Apifon’s Service Control Panel (Mookee) and will be given to you via email.
- Each generated token maps directly to your account, message route, sender IDs and IP restrictions.
- A set of IPs can be associated with a token, which restricts requests using that token to be sent exclusively from those IPs. If no IPs are specified, your token can be used from anywhere on the Internet.
- Your account can have multiple tokens.
- Tokens do not expire, and can be edited at any time.
- Make sure not to disclose any of your tokens to any unauthorized entities. If this happens, tokens can be invalidated (deleted) from the same user interface. Once a token is invalidated, it cannot be re-used again, instead a new one has to be generated.
The Authentication Header
Authorization: ApifonWS [Token]:[Signature]
Setting Authorization Header Code Example
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpPost;
HttpPost request = new HttpPost();
request.setHeader("Authorization", "ApifonWS " + token + ":" + signature);
$curl = curl_init($url);
$header[] = "Authorization: ApifonWS " . $token . ":" . $signature;
curl_setopt($curl, CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER, $header);
WebRequest webRequest = WebRequest.Create(uri);
webRequest.Headers["Authorization"] = "ApifonWS " + token + ":" + signature;
headers = {
"Authorization": "ApifonWS %s: %s" % (token, signature),
}
connection = http.client.HTTPConnection(base_url)
connection.request(method, endpoint, body, headers)
var request = require('sync-request');
var res = request(method, url, {
headers: {
'Authorization': 'ApifonWS ' + token + ":" + signature,
},
body: body
});
The ApifonWS REST API uses the standard HTTP Authorization header to pass authentication information. (The name of the standard header is unfortunate because it carries authentication information, not authorization.) Under the ApifonWS authentication scheme, the Authorization header has the following form:
When developers register they are issued an ApifonWS token and ApifonWS secret access key. For request authentication, the ApifonWS token element is used to indirectly retrieve the secret key to compute the signature and, thus, identify the developer making the request.
Authorization Instructions:
Authorization = "ApifonWS" + " " + Token + ":" + Signature
Signature = Base64( HMAC-SHA256( YourSecretAccessKeyID, UTF-8-Encoding-Of( StringToSign ) ) );
StringToSign = HTTP-Verb + "\n"
+ HTTP-Request-Uri + "\n"
+ Content(Body) + "\n"
+ Date
Building Signature Code Example
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import javax.crypto.Mac;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Base64;
public class SignatureGenerator {
public static String getSignature(String secretKey, String method, String uri, String body, String strDate){
String toSign = method + "\n"
+ uri + "\n"
+ body + "\n"
+ strDate;
Mac mac = null;
try {
byte[] secretyKeyBytes = secretKey.getBytes("UTF-8");
SecretKeySpec secretKeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(secretyKeyBytes, "HmacSHA256");
mac = Mac.getInstance("HmacSHA256");
mac.init(secretKeySpec);
} catch (Exception ex) {
System.out.println(ex);
}
String signature = null;
byte[] data;
byte[] rawHmac;
try {
data = toSign.getBytes("UTF-8");
rawHmac = mac.doFinal(data);
Base64 encoder = new Base64();
signature = new String(encoder.encode(rawHmac));
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("UTF-8 is unsupported!", e);
}
return signature;
}
}
$message = $method."\n"
. $endpoint . "\n"
. $body . "\n"
. $requestDate;
$signature = base64_encode(hash_hmac('SHA256', $message, $secretKey, true));
using System;
using System.Security.Cryptography;
namespace Apifon
{
class SignatureGenerator
{
public static string hmac(string secretKey, string method, string uri, string body, string strDate)
{
string toSign = method + "\n"
+ uri + "\n"
+ body + "\n"
+ strDate;
var encoding = new System.Text.UTF8Encoding();
byte[] keyByte = encoding.GetBytes(secretKey);
byte[] messageBytes = encoding.GetBytes(toSign);
using (var hmacsha256 = new HMACSHA256(keyByte))
{
byte[] hashmessage = hmacsha256.ComputeHash(messageBytes);
return Convert.ToBase64String(hashmessage);
}
}
}
}
import base64
import hashlib
import hmac
def sign(method, endpoint, body, request_date, secretKey):
try:
signed_message = method + "\n" + endpoint + "\n" + body + "\n" + request_date
encode = hmac.new(bytes(secretKey.encode("utf-8")), bytes(signed_message.encode("utf-8")), hashlib.sha256).digest()
signature = base64.b64encode(encode).decode()
return signature
except Exception as e:
print(str(e))
var message = method + "\n"
+ endpoint + "\n"
+ body + "\n"
+ requestDate;
var signature = crypto.createHmac('sha256', secretKey).update(message).digest('base64');
The Signature element is the RFC 2104 HMAC-SHA256 of selected elements from the request, meaning that the Signature part of the Authorization header will vary from request to request. If the request signature calculated by the system matches the Signature included with the request, the requester will have demonstrated possession of the ApifonWS secret access key. The request will then be processed under the identity, and with the authority of the developer to whom the key was issued.
Following is a pseudogrammar that illustrates the construction of the Authorization request header. (In the example, \n means the Unicode code point U+000A, commonly called newline).
HMAC-SHA256 is an algorithm defined by RFC 2104 – Keyed-Hashing for Message Authentication . The algorithm takes as input two byte-strings, a key and a message. For ApifonWS request authentication, use your ApifonWS secret access key (YourSecretAccessKeyID) as the key, and the UTF-8 encoding of the StringToSign as the message. The output of HMAC-SHA256 is also a byte string, called the digest. The Signature request parameter is constructed by Base64 encoding this digest.
Request Canonicalization for Signing
Recall that when the system receives an authenticated request, it compares the computed request signature to the signature provided by the StringToSign of the request. For that reason, you must compute the signature by using the same method used by ApifonWS. We call the process of putting a request in an agreed-upon form for signing canonicalization.
String to sign empty Elements
If a StringToSign element called for in the definition of StringToSign is not present in your request (for example, Content are optional for PUT requests and meaningless for GET requests), substitute the empty string (“”) for that position.
Time Stamp Requirement
Building Timestamp Header Code Example
HttpPost request = new HttpPost();
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("EEE, dd MMM yyyy HH:mm:ss z", Locale.US);
dateFormat.setTimeZone(TimeZone.getTimeZone("GMT"));
String strDate = dateFormat.format(new Date());
request.setHeader("X-ApifonWS-Date", strDate);
$dateTime = new \DateTime();
$dateTime->setTimezone(new \DateTimeZone('GMT'));
$requestDate = $dateTime->format('D, d M Y H:i:s T');
$header[] = "X-ApifonWS-Date: " . $requestDate;
curl_setopt($curl, CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER, $header);
String strDate = DateTime.Now.ToUniversalTime().ToString("r");
WebRequest webRequest = WebRequest.Create(uri);
webRequest.Headers["X-ApifonWS-Date"] = strDate;
request_date = datetime.now(timezone.utc).strftime('%a, %d %b %Y %H:%M:%S GMT')
headers = {
"X-ApifonWS-Date": request_date
}
connection = http.client.HTTPConnection(base_url)
connection.request(method, endpoint, body, headers)
var d = new Date();
var dateTime = d.toUTCString();
var requestDate = dateTime;
var request = require('sync-request');
var res = request(method, url, {
headers: {
'X-ApifonWS-Date': requestDate
},
body: body
});
A valid time stamp (use only an X-ApifonWS-Date header) is mandatory for authenticated requests. Furthermore, the client timestamp included with an authenticated request must be within 15 minutes of the ApifonWS system time when the request is received. If not, the request will fail with the Unauthorized (or 401 Unauthorized Access) error code. The intention of these restrictions is to limit the possibility that intercepted requests could be replayed by an adversary. For stronger protection against eavesdropping, use the HTTPS transport for authenticated requests.
You can set the timestamp for the request by using an ‘X-ApifonWS-Date’ header. The value of the X-ApifonWS-Date header must be in one of the RFC 2616 formats (http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2616.txt). See the next section for an example.
Authentication Examples
Setting Authorization Header Code Example
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpPost;
HttpPost request = new HttpPost();
request.setHeader("Authorization", "ApifonWS " + token + ":" + signature);
$curl = curl_init($url);
$header[] = "Authorization: ApifonWS " . $token . ":" . $signature;
curl_setopt($curl, CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER, $header);
WebRequest webRequest = WebRequest.Create(uri);
webRequest.Headers["Authorization"] = "ApifonWS " + token + ":" + signature;
headers = {
"Authorization": "ApifonWS %s: %s" % (token, signature),
}
connection = http.client.HTTPConnection(base_url)
connection.request(method, endpoint, body, headers)
var request = require('sync-request');
var res = request(method, url, {
headers: {
'Authorization': 'ApifonWS ' + token + ":" + signature,
},
body: body
});
The examples in this section use the (non-working) credentials in the following table.
| Parameter | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Token | 5b5a6ca0deb4bdba5bab | An alphanumeric sequence that is used to reference to the user Account a is making the Request. |
| Secret Key | YourSecretKey | A character sequence used to validate the identity of the Requester. |
In the example StringToSign, formatting is not significant, and \n means the Unicode code point U+000A, commonly called newline. Also, the examples use “+0000” to designate the timezone. You can use “GMT” to designate timezone instead, but the signatures shown in the examples will be different.
Example Object POST
Request
Method: POST
Endpoint: /services/sms/send
Content-Type: application/json
Content-Length: 12
Host: ars.apifon.com
X-ApifonWS-Date: Sun, 22 Feb 2016 21:29:42 +0000
Authorization: ApifonWS 5b5a6ca0deb4bdba5bab:YourSecretKey
StrToSign
POST \n
/services/sms/send \n
{”subscribers”:{...}, ”message”:{...}, ...} \n
Sun, 22 Feb 2016 21:29:42 +0000
Complete Request Example
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URI;
import java.net.URISyntaxException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.TimeZone;
import org.apache.http.HttpResponse;
import org.apache.http.client.HttpClient;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpPost;
import org.apache.http.entity.StringEntity;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.HttpClientBuilder;
public class HttpRequest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws URISyntaxException, IOException {
String token = "5b5a6ca0deb4bdba5bab";
String secretKey = "YourSecretKey";
String endpoint = "/services/balance";
String body = "";
StringEntity input = new StringEntity(body, "UTF-8");
input.setContentType("application/json");
HttpPost request = new HttpPost();
request.setEntity(input);
request.setURI(new URI("https://ars.apifon.com" + endpoint));
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("EEE, dd MMM yyyy HH:mm:ss z", Locale.US);
dateFormat.setTimeZone(TimeZone.getTimeZone("GMT"));
String strDate = dateFormat.format(new Date());
HttpClient httpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create().build();
URI tmUri = new URI(endpoint);
String signature = SignatureGenerator.getSignature(secretKey, "POST", tmUri.getPath(), body, strDate);
request.setHeader("Content-Type", "application/json");
request.setHeader("Authorization", "ApifonWS " + token + ":" + signature);
request.setHeader("X-ApifonWS-Date", strDate);
HttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(request);
}
}
<?php
$token = "5b5a6ca0deb4bdba5bab";
$secretKey = "YourSecretKey";
$endpoint = "/services/balance";
$body = "";
$url = "https://ars.apifon.com" . $endpoint;
$dateTime = new \DateTime();
$dateTime->setTimezone(new \DateTimeZone('GMT'));
$requestDate = $dateTime->format('D, d M Y H:i:s T');
$message = "POST"."\n"
. $endpoint . "\n"
. $body . "\n"
. $requestDate;
$signature = base64_encode(hash_hmac('SHA256', $message, $secretKey, true));
$header = array();
$header[] = "Content-type: application/json";
$header[] = "Authorization: ApifonWS " . $token . ":" . $signature;
$header[] = "X-ApifonWS-Date: " . $requestDate;
$curl = curl_init($url);
curl_setopt($curl, CURLOPT_SSL_VERIFYHOST, false);
curl_setopt($curl, CURLOPT_SSL_VERIFYPEER, false);
curl_setopt($curl, CURLOPT_HEADER, false);
curl_setopt($curl, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, true);
curl_setopt($curl, CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER, $header);
curl_setopt($curl, CURLOPT_POST, true);
curl_setopt($curl, CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS, $body);
$response = curl_exec($curl);
using System;
using System.Security.Cryptography;
using System.IO;
using System.Net;
using System.Text;
namespace Apifon
{
class HttpRequest
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
String token = "5b5a6ca0deb4bdba5bab";
String secretKey = "YourSecretKey";
String body = "";
String uri = "https://ars.apifon.com/services/balance";
String strDate = DateTime.Now.ToUniversalTime().ToString("r");
byte[] data = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(body);
WebRequest webRequest = WebRequest.Create(uri);
Uri tmpUri = new Uri(uri);
webRequest.Method = "POST";
webRequest.ContentType = "application/json";
webRequest.ContentLength = data.Length;
string toSign = "POST" + "\n"
+ tmpUri.AbsolutePath + "\n"
+ body + "\n"
+ strDate;
string signature;
var encoding = new UTF8Encoding();
byte[] messageBytes = encoding.GetBytes(toSign);
using (var hmacsha256 = new HMACSHA256(encoding.GetBytes(secretKey)))
{
signature = Convert.ToBase64String(hmacsha256.ComputeHash(messageBytes));
}
webRequest.Headers["X-ApifonWS-Date"] = strDate;
webRequest.Headers["Authorization"] = "ApifonWS " + token + ":" + signature;
using (Stream stream = webRequest.GetRequestStream())
{
stream.Write(data, 0, data.Length);
}
string responseContent = null;
using (WebResponse response = webRequest.GetResponse())
{
using (Stream stream = response.GetResponseStream())
{
using (StreamReader sr99 = new StreamReader(stream))
{
responseContent = sr99.ReadToEnd();
}
}
}
Console.WriteLine(responseContent);
}
}
}
import json
import base64
import hashlib
import hmac
import http.client
from datetime import datetime, timezone
request_date = datetime.now(timezone.utc).strftime('%a, %d %b %Y %H:%M:%S GMT')
token = "5b5a6ca0deb4bdba5bab"
secretKey = "YourSecretKey"
uri = "ars.apifon.com"
endpoint = "/services/balance"
body = ""
signed_message = "POST" + "\n" + endpoint + "\n" + body + "\n" + request_date
encode = hmac.new(bytes(secretKey.encode("utf-8")), bytes(signed_message.encode("utf-8")), hashlib.sha256).digest()
signature = base64.b64encode(encode).decode()
headers = {
"Content-type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "ApifonWS %s: %s" % (token, signature),
"X-ApifonWS-Date": request_date
}
try:
connection = http.client.HTTPConnection(uri)
connection.request("POST", endpoint, body, headers)
except Exception as e:
print(str(e))
t = json.loads(connection.getresponse().read().decode('utf8'))
print(t)
var token = "5b5a6ca0deb4bdba5bab";
var secretKey = "YourSecretKey";
var endpoint = "/services/balance";
var body = "";
var url = "https://ars.apifon.com" + endpoint;
var requestDate = new Date().toUTCString();
var message = "POST" + "\n"
+ endpoint + "\n"
+ body + "\n"
+ requestDate;
const crypto = require('crypto');
var signature = hmac = crypto.createHmac('sha256', secretKey).update(message).digest('base64');
var request = require('sync-request');
var res = request("POST", url, {
headers: {
'Content-type': 'application/json',
'Authorization': 'ApifonWS ' + token + ":" + signature,
'X-ApifonWS-Date': requestDate,
},
body: body
});
return JSON.parse(res.getBody('utf8'));
This example sends an SMS request with the POST method.
REST Request Signing Problems
When REST request authentication fails, the system responds to the request with an 401 Unauthorized Error.
Some toolkits silently insert headers that you do not know about beforehand, such as adding the header Content-Type during a POST. In most of these cases, the value of the inserted header remains constant, allowing you to discover the missing headers by using tools such as Ethereal or tcpmon.
Using Base64 Encoding
HMAC request signatures must be Base64 encoded. Base64 encoding converts the signature into a simple ASCII string that can be attached to the request.
OAuth2 Authentication
To access REST APIs using OAuth2 tokens, you must supply with each request a Bearer token in the HTTP Authorization header.
To generate a Bearer token you will need a set of credentials (Client ID & Client Secret).
To generate your set of credentials, log in to Apifon’s Service Control Panel (Mookee) and create an OAuth token.
- Your set of credentials never expire.
- Bearer tokens once issued, expire after one day for security reasons.
- The API does not support refresh tokens on
client_credentialsgrant type.
A fresh Bearer token must be issued in case of Bearer token revocation/expiration.
- Each set of credentials maps directly to your account, message route, sender IDs, IP restrictions and scope restrictions.
- Your account can have multiple sets of credentials.
- A set of IPs can be associated with your credentials, which restricts requests from Bearer tokens generated using those credentials.
If no IPs are specified, your bearer tokens can be used from anywhere on the Internet.
- Each set of credentials can be restricted on which resource(s) any generated Bearer token can access.
Optionally during the issue of Bearer tokens the requested token scopes can be modified to further restrict access for a generated token.
For more information refer to the Scopes section. - Your set of credentials as well as any Bearer tokens issued are CONFIDENTIAL and MUST NOT be disclosed to unauthorized entities.
- If you suspect that your Bearer tokens and/or credentials are compromised, Bearer tokens can be revoked and credentials can be deleted from the User Interface.
Please note that deleting the set of credentials will invalidate all Bearer tokens issued using those credentials. - Once revoked or expired, Bearer tokens can't be reused and a new Bearer token must be generated.
- If you suspect that your Bearer tokens and/or credentials are compromised, Bearer tokens can be revoked and credentials can be deleted from the User Interface.
OAuth2 Flow
With machine-to-machine (M2M) applications, such as services running on your backend, the system authenticates and authorizes the application rather than a user.
Our service currently supports the Client Credentials Flow (defined in OAuth 2.0 RFC 6749, section 4.4). For this flow to operate a client must pass along their Client ID and Client Secret to the Identity Service to authenticate themselves and retrieve a token.
This token (referred as Bearer token) is subsequently used when directing calls to Apifon's REST API.
The following diagram demonstrates the flow:
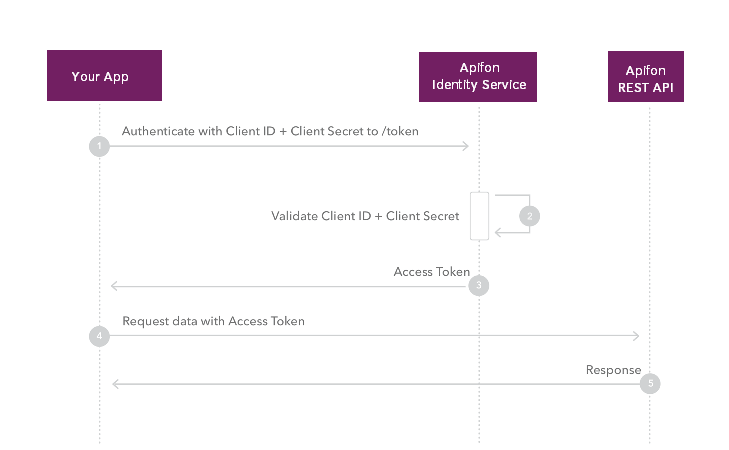
Your application sends a request to Apifon Identity Service (/oauth2/token) passing grant type, client ID, client Secret and optionally requested scopes as parameters.
To learn more about Scopes refer to the Scopes section.Apifon's Identity Service validates your credentials.
Apifon's Identity Service issues a Bearer token and responds.
Your application uses the Bearer token previously issued to call Apifon's API on behalf of itself.
The API responds with the requested data.
Scopes
Each scope provides access to specific endpoints on Apifon's platform. Scopes are defined both when issuing a set of credentials through the Control Panel (Mookee) and when requesting a Bearer token from the Identity Service.
Scopes are applied on endpoint-level on Apifon's platform. You can find out what scopes each endpoint requires in the API reference.
Some scopes may extend another scope. For example WRITE scope on some resources extends the READ scope of the same resource. For scopes that are extending another scope the API assumes that the extended scope is the scope of your Bearer token. Your Bearer token request in this case may not contain the scope that it extends.
If you wish to include scopes in your token request consider the following:
- Scopes are optional and can be used to further restrict what resource(s) a generated Bearer token can access.
- By default, issuing a token with no scopes specified grants the Bearer token all of the scopes supported by your set of credentials.
- Multiple scopes are allowed on Bearer tokens.
- Issuing a Bearer token with specific scopes means that your request MUST carry the scope(s) that the endpoint you are trying to access requires.
- Your set of credentials MUST allow each scope carried by the Bearer token.
- If a scope present in your Bearer token is no longer granted by your credentials (even if not explicitly required by the endpoint) this will result in an
401 - Unauthorizedexception and a new Bearer token must be generated.
- If a scope present in your Bearer token is no longer granted by your credentials (even if not explicitly required by the endpoint) this will result in an
- Your application will be responsible for checking and handling any scopes that you are not authorized for.
The following is a list of Scopes supported by the API. This document will reflect any additional scopes supported by the API and you are advised to check back regularly.
| Scope | SDK Scope | Description | Extends |
|---|---|---|---|
| accountInfo | ACCOUNT_INFO | Read permission on information regarding your account, eg. balance. Bearer tokens with this scope can access information regarding your account setup |
- |
| readList | READ_LIST | Read permission on the /list resource. Bearer tokens with this scope can access information regarding your lists but can't modify them. |
- |
| writeList | WRITE_LIST | Full permission on the /list resource. Bearer tokens with this scope are granted create, edit and delete permissions on your lists. |
readList |
| readSubscriber | READ_SUBSCRIBER | Read permission on the /subscriber resource. Bearer tokens with this scope can access information regarding your subscribers but can't modify them |
- |
| writeSubscriber | WRITE_SUBSCRIBER | Full permission on the /subscriber resource. Bearer tokens with this scope are granted create, edit and delete permissions on your lists. |
readSubscriber |
| smsGateway | SMS_GATEWAY | API access on the /sms resource. Bearer tokens with this scope can access the SMS Gateway on your behalf. |
- |
| imGateway | IM_GATEWAY | API access on the /im resource. Bearer tokens with this scope can access the IM Gateway on your behalf. |
- |
| otpGateway | OTP_GATEWAY | API access on the /otp resource. Bearer tokens with this scope can dispatch and verify OTP requests on your behalf. |
- |
Bearer Token Request
Request headers
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Request URI
https://ids.apifon.com/oauth2/token
Request Body (When used as POST request with body)
grant_type=client_credentials&client_id=YOUR_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET&scope=accountInfo+imGateway+smsGateway
Query Parameters (When used as a POST request with query parameters)
https://ids.apifon.com/oauth2/token?grant_type=client_credentials&client_id=YOUR_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET&scope=accountInfo+imGateway+smsGateway
Request examples
var client_id = "{YOUR_CLIENT_ID}";
var client_secret = "{YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET}";
var requested_scopes = "{YOUR_REQUESTED_SCOPES}";
var body = "grant_type=client_credentials&client_id=CLIENT_ID&client_secret=CLIENT_SECRET&scopes=REQUESTED_SCOPES"
.replace("CLIENT_ID", client_id)
.replace("CLIENT_SECRET", client_secret)
.replace("REQUESTED_SCOPES", requested_scopes);
var url = "https://ids.apifon.com/oauth2/token";
var request = require('sync-request');
var res = request("POST", url, {
headers: {
'Content-type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'
},
body: body
});
return JSON.parse(res.getBody('utf8'));
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Net;
using System.Text;
namespace Apifon
{
public class BearerTokenRequest
{
static string IDENTITY_SERVICE_URI = "https://ids.apifon.com/oauth2/token";
static string CLIENT_ID = "{YOUR_CLIENT_ID}";
static string CLIENT_SECRET = "{YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET}";
static string REQUESTED_SCOPES = "{YOUR_REQUESTED_SCOPES}";
static String requestBearerAccessToken()
{
WebRequest webRequest = WebRequest.Create(IDENTITY_SERVICE_URI);
string postData = "grant_type=client_credentials&client_id=CLIENT_ID&client_secret=CLIENT_SECRET&scopes=REQUESTED_SCOPES"
.Replace("CLIENT_ID", CLIENT_ID)
.Replace("CLIENT_SECRET", CLIENT_SECRET)
.Replace("REQUESTED_SCOPES", REQUESTED_SCOPES);
byte[] dataStream = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(postData);
webRequest.Method = "POST";
webRequest.ContentType = "application/x-www-form-urlencoded";
webRequest.ContentLength = dataStream.Length;
using (Stream stream = webRequest.GetRequestStream())
{
stream.Write(dataStream, 0, dataStream.Length);
}
string responseContent = null;
using (WebResponse response = webRequest.GetResponse())
{
using (Stream stream = response.GetResponseStream())
{
using (StreamReader sr99 = new StreamReader(stream))
{
responseContent = sr99.ReadToEnd();
}
}
}
return responseContent;
}
}
}
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URI;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.http.NameValuePair;
import org.apache.http.client.entity.UrlEncodedFormEntity;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.CloseableHttpResponse;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpPost;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.HttpClientBuilder;
import org.apache.http.message.BasicNameValuePair;
import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils;
public class RequestAccessToken {
private static final String IDENTITY_SERVICE_URI = "https://ids.apifon.com/oauth2/token";
private static final String GRANT_TYPE = "client_credentials";
private static final String CLIENT_ID = "{YOUR_CLIENT_ID}";
private static final String CLIENT_SECRET = "{YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET}";
private static final String REQUESTED_SCOPES = "{YOUR_REQUESTED_SCOPES}";
// Use this if you want to send a POST request with parameters encoded in the body.
public static String requestAccessTokenWithPostParameters() throws IOException {
List<NameValuePair> postParameters = new ArrayList<>();
postParameters.add(new BasicNameValuePair("grant_type", GRANT_TYPE));
postParameters.add(new BasicNameValuePair("client_id", CLIENT_ID));
postParameters.add(new BasicNameValuePair("client_secret", CLIENT_SECRET));
postParameters.add(new BasicNameValuePair("scope", REQUESTED_SCOPES));
try (CloseableHttpClient client = HttpClientBuilder.create().build()) {
HttpPost tokenRequest = new HttpPost(URI.create(IDENTITY_SERVICE_URI));
tokenRequest.setHeader("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
tokenRequest.setEntity(new UrlEncodedFormEntity(postParameters, StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
try (CloseableHttpResponse httpResponse = client.execute(tokenRequest)) {
if (httpResponse.getEntity() != null) {
String response = EntityUtils.toString(httpResponse.getEntity(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
EntityUtils.consumeQuietly(httpResponse.getEntity());
return response;
}
throw new IOException("Received null response from identity service");
}
}
}
// Use this if you want to send a POST request with no body where the parameters are send as query parameters.
public static String requestAccessTokenWithPostQueryParameters() throws IOException, URISyntaxException {
URI requestURI = new URIBuilder(URI.create(IDENTITY_SERVICE_URI))
.addParameter("grant_type", GRANT_TYPE)
.addParameter("client_id", CLIENT_ID)
.addParameter("client_secret", CLIENT_SECRET)
.addParameter("scope", REQUESTED_SCOPES)
.build();
try (CloseableHttpClient client = HttpClientBuilder.create().build()) {
HttpPost tokenRequest = new HttpPost(requestURI);
tokenRequest.setHeader("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
try (CloseableHttpResponse httpResponse = client.execute(tokenRequest)) {
if (httpResponse.getEntity() != null) {
String response = EntityUtils.toString(httpResponse.getEntity(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
EntityUtils.consumeQuietly(httpResponse.getEntity());
return response;
}
throw new IOException("Received null response from identity service");
}
}
}
}
Identity Service Host URL: https://ids.apifon.com
Token Endpoint: /oauth2/token
HTTP Method: POST
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
To retrieve a Bearer token from the Identity Service you will need an active set of credentials (Client ID & Client Secret).
To create your credentials, login to the Control Panel (Mookee) and navigate to your account tokens.
| Key | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| client_id | String | The client ID retrieved from OAuth token in Control Panel |
| client_secret | String | The client secret retrieved from OAuth token in Control Panel |
| scope (Optional) | String | The requested scopes, depending on the application needs. Each scope must be seperated by an empty space. Refer to the Scopes documentation. |
| grant_type | String | The grant type. Only client_credentials is currently supported |
No specific order of parameters is specified. Any additional parameters provided, beyond those mentioned, are ignored and have no effect on the result of the call.
Your request to retrieve the Bearer token can be either in the form of a request with a body OR a request with no body where the parameters are sent as query parameters in the URI.
Bearer Token Response
Response headers
Content-Type: application/json
Cache-Control: no-store
Pragma: no-cache
X-Frame-Options: Deny
X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff
X-XSS-Protection: 1; mode=block
Date: Wed, 04 Mar 2020 15:20:15 GMT
Response sample
{
"access_token": "2ef88b5b-73aa-3051-9451-7b611c08323c",
"scope": "accountInfo imGateway smsGateway",
"token_type": "Bearer",
"expires_in": 315569260
}
Successful response HTTP Status Code: 200
Content-Type: application/json
A succesful response follows the specification of section 5.1 of the OAuth 2.0 RFC 6749
An error response follows the specification of section 5.2 of the OAuth 2.0 RFC 6749
Success JSON Response
If your request to generate a Βearer token is successful you will receive a response with a 200 - OK HTTP Status Code.
The response format is the following
| Key | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| access_token | String | The Βearer token issued by the identity service |
| scope (Conditional) | String | The scopes that the generated token carries. Each scope is seperated with an empty space character. This field may be missing from the response if your initial issue request doesn't include specific scopes. |
| token_type | String | The type of the token. Only Bearer is supported |
| expires_in | Integer | The validity period of the access_token in seconds |
Error Response
Error response sample
Missing grant_type
{
"error_description": "OAuthProblemException{error='invalid_request', description='Missing grant_type parameter value', uri='null', state='null', scope='null', redirectUri='null', responseStatus=0, parameters={}}",
"error": "invalid_request"
}
Invalid credentials
{
"error_description": "A valid OAuth client could not be found for client_id: RqPAhu56rGCrkGPqy8EG8EO4BQQ8G7V1uhSQVDkuovo6TUVupRIYqFb6lekMLaCK1",
"error": "invalid_client"
}
Invalid scope
{
"error_description": "Invalid Scope!",
"error": "invalid_scope"
}
If your request is unsuccessful you will receive a response with a 400 - Bad Request HTTP Status Code.
The error response format is the following
| Key | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| error_description | String | Human-readable text providing additional information regarding the error. Useful for troubleshooting the cause of the error. |
| error | String | The error code. For possible values please refer to the OAuth 2.0 specification. |
Other response codes
| HTTP Status Code | Description | Troubleshooting |
|---|---|---|
| 404 | Not Found | Service currently unavailable. Please retry later. |
| 405 | Method Not Allowed | Make sure the HTTP Method is POST. |
| 415 | Unsupported Media Type | Make sure the Content-Type header is set to application/x-www-form-urlencoded |
| 500 | Internal Server Error | Something went wrong with your request. Please retry the request. |
If the error persists please contact us
Using Bearer Tokens
Authorization Header
Authorization: Bearer 2ef88b5b-73aa-3051-9451-7b611c08323c
After generating a Bearer token you can use it to access Apifon's REST API.
Bearer Tokens generated from the Identity Service follow the OAuth 2.0 RFC 6750 Bearer Token Usage specification.
Apifon's REST API supports ONLY the Authorization Request Header Field as described in the Bearer Token Usage Specification
Section 2.1 of the OAuth 2.0 RFC 6750.
The Bearer Bearer Token generated MUST be included in the Authorization HTTP header of your request in order to access a resource.
The API will consume your Bearer token, validate it, and if you are authorized to access the resource will respond accordingly. Please refer to the API Reference for endpoint-specific responses.
Unauthorized Attempts
Unauthorized Response Header (Invalid Token)
WWW-Authenticate: Bearer error="invalid_token"
Unauthorized Response Header (Invalid Scope/Not authorized to access scope)
WWW-Authenticate: Bearer error="invalid_scope"
If your token is invalid or there is something wrong related to your Bearer Authentication Token a 401 - Unauthorized HTTP status code will be signaled back.
The response will include a WWW-Authenticate HTTP Header including a general description of the error.
This may happen if your token carries Scopes that is not allowed to access, the Bearer token has been revoked or has expired.
Revoked/Invalid tokens MUST NOT be used to access a resource.
Your application MUST be properly configured to handle those cases. The best course of action in this case is trying to issue a new Bearer Token from the Identity Service. In case the new token request fails as well, that means that your credentials are probably invalid and should be validated again from the Control Panel.
Revoke a Bearer Token
Request headers
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Request URI
https://ids.apifon.com/oauth2/revoke
Request Body (When used as POST request with body)
client_id=YOUR_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET&token=YOUR_BEARER_TOKEN
Query Parameters (When used as a POST request with query parameters)
https://ids.apifon.com/oauth2/revoke?client_id=YOUR_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET&token=YOUR_BEARER_TOKEN
Request examples
var client_id = "{YOUR_CLIENT_ID}";
var bearer_token = "{YOUR_BEARER_TOKEN}";
var body = "client_id=CLIENT_ID&token=BEARER_TOKEN"
.replace("CLIENT_ID", client_id)
.replace("BEARER_TOKEN", bearer_token);
var url = "https://ids.apifon.com/oauth2/revoke";
var request = require('sync-request');
var res = request("POST", url, {
headers: {
'Content-type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'
},
body: body
});
return JSON.parse(res.getBody('utf8'));
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Net;
using System.Text;
namespace Apifon
{
public class BearerTokenRevocation
{
static string IDENTITY_SERVICE_URI = "https://ids.apifon.com/oauth2/revoke";
static string CLIENT_ID = "{YOUR_CLIENT_ID}";
static string BEARER_TOKEN = "{YOUR_BEARER_TOKEN}";
static String revokeBearerToken()
{
WebRequest webRequest = WebRequest.Create(IDENTITY_SERVICE_URI);
string postData = "client_id=CLIENT_ID&token=TOKEN"
.Replace("CLIENT_ID", CLIENT_ID)
.Replace("TOKEN", BEARER_TOKEN);
byte[] dataStream = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(postData);
webRequest.Method = "POST";
webRequest.ContentType = "application/x-www-form-urlencoded";
webRequest.ContentLength = dataStream.Length;
using (Stream stream = webRequest.GetRequestStream())
{
stream.Write(dataStream, 0, dataStream.Length);
}
string responseContent = null;
using (WebResponse response = webRequest.GetResponse())
{
using (Stream stream = response.GetResponseStream())
{
using (StreamReader sr99 = new StreamReader(stream))
{
responseContent = sr99.ReadToEnd();
}
}
}
return responseContent;
}
}
}
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URI;
import java.net.URISyntaxException;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.http.NameValuePair;
import org.apache.http.client.entity.UrlEncodedFormEntity;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.CloseableHttpResponse;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpPost;
import org.apache.http.client.utils.URIBuilder;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.HttpClientBuilder;
import org.apache.http.message.BasicNameValuePair;
import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils;
public class RevokeTokenRequest {
private static final String IDENTITY_SERVICE_URI = "https://ids.apifon.com/oauth2/revoke";
private static final String CLIENT_ID = "{YOUR_CLIENT_ID}";
private static final String BEARER_TOKEN = "{YOUR_BEARER_TOKEN}";
// Use this if you want to send a POST request with parameters encoded in the body.
public static void revokeAccessTokenWithPostParameters() throws IOException {
List<NameValuePair> postParameters = new ArrayList<>();
postParameters.add(new BasicNameValuePair("client_id", CLIENT_ID));
postParameters.add(new BasicNameValuePair("token", BEARER_TOKEN));
try (CloseableHttpClient client = HttpClientBuilder.create().build()) {
HttpPost tokenRequest = new HttpPost(URI.create(IDENTITY_SERVICE_URI));
tokenRequest.setHeader("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
tokenRequest.setEntity(new UrlEncodedFormEntity(postParameters, StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
try (CloseableHttpResponse httpResponse = client.execute(tokenRequest)) {
String response = EntityUtils.toString(httpResponse.getEntity(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
EntityUtils.consumeQuietly(httpResponse.getEntity());
if (200 != httpResponse.getStatusLine().getStatusCode()) {
throw new IOException("Received invalid response " + response + " from Identity Service"
+ " Status code is : " + String.valueOf(httpResponse.getStatusLine().getStatusCode()));
}
}
}
}
// Use this if you want to send a POST request with no body where the parameters are send as query parameters.
public static void revokeAccessTokenWithPostQueryParameters() throws IOException, URISyntaxException {
URI requestURI = new URIBuilder(URI.create(IDENTITY_SERVICE_URI))
.addParameter("client_id", CLIENT_ID)
.addParameter("token", BEARER_TOKEN)
.build();
try (CloseableHttpClient client = HttpClientBuilder.create().build()) {
HttpPost tokenRequest = new HttpPost(requestURI);
tokenRequest.setHeader("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
try (CloseableHttpResponse httpResponse = client.execute(tokenRequest)) {
String response = EntityUtils.toString(httpResponse.getEntity(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
EntityUtils.consumeQuietly(httpResponse.getEntity());
if (200 != httpResponse.getStatusLine().getStatusCode()) {
throw new IOException("Received invalid response " + response + " from Identity Service"
+ " Status code is : " + String.valueOf(httpResponse.getStatusLine().getStatusCode()));
}
}
}
}
}
In case you no longer need a previously issued Bearer token or you suspect that your token is compromised by an unauthorized party you can revoke it. The API supports the token revocation specification of OAuth 2.0 RFC 7009
Identity Service Host URL: https://ids.apifon.com
Token Endpoint: /oauth2/revoke
HTTP Method: POST
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Your revocation request MUST contain the following to succeed.
| Key | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| client_id | String | The client ID retrieved from OAuth token in Control Panel |
| token | String | The token you wish to revoke |
No specific order of parameters is specified. Any additional parameters provided, beyond those mentioned, are ignored and have no effect on the result of the call.
The request to revoke a Bearer token can be either in the form of a request with a body OR a request with no body where the parameters are sent as query parameters in the URI.
In case of a succesful revocation, a 200 - OK will be signaled back.
Please note that this call can only fail if the request to revoke a token doesn't contain a required parameter.
Incorrect parameters (eg. invalid credentials and/or invalid token) and are not signaled back to the client as an error for security reasons.
Your token may not be revoked in this case.
In case you are missing a required parameter the following will be signaled back
- Missing client Credentials
HTTP Status Code: 401 - Unauthorized
Header Content-Type: text/html
Body: {"error_description":"Client Authentication failed.","error":"invalid_client"}
- Missing token
HTTP Status Code: 400 - Bad Request
Header Content-Type: text/html
Body: {"error_description":"Invalid revocation request","error":"invalid_request"}

